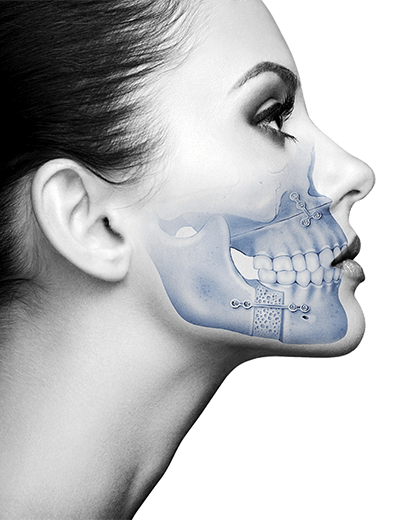
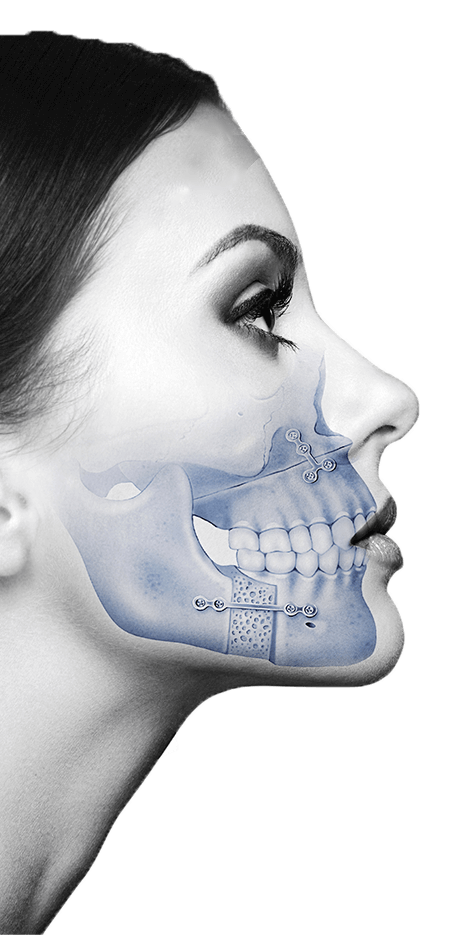
Paediatric maxillofacial surgery encompasses surgery of the entire facial structure, including both soft and hard tissue, in children and adolescents. The surgical team at the Maxillofacial Institute are specialised in performing maxillofacial surgery for infants, children, and adolescents, and can treat both congenital malformations and acquired problems.
The most common interventions in paediatric oral and maxillofacial surgery are the following: