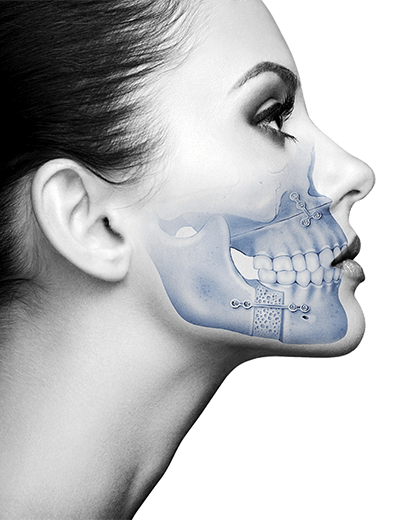
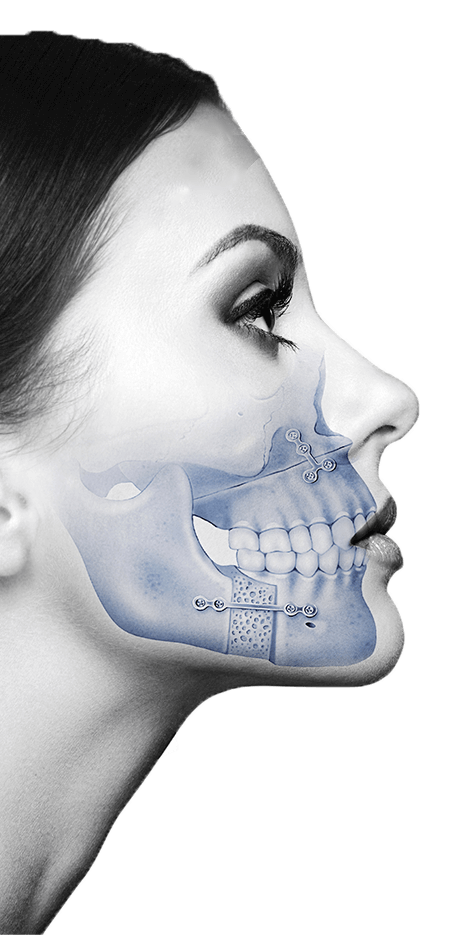
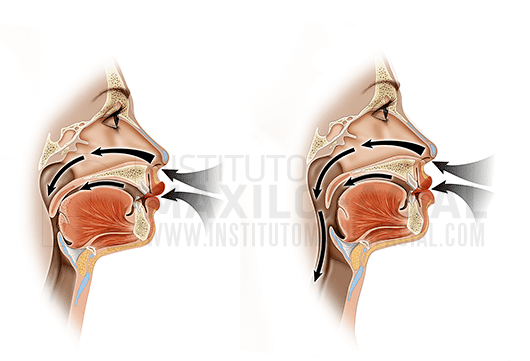
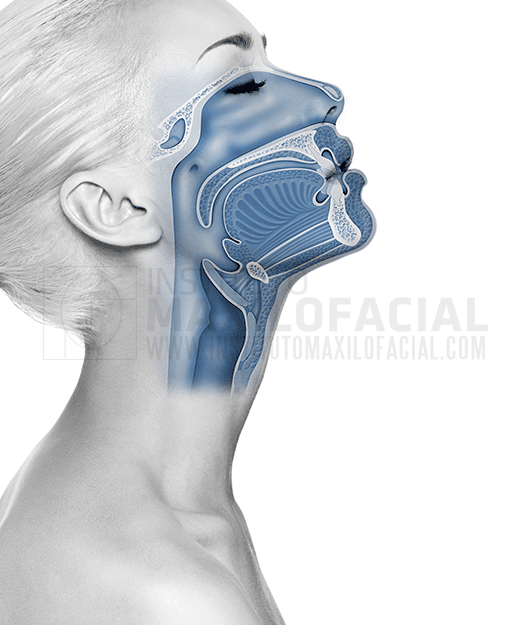
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OAS) is a disorder consisting of repeated episodes of pauses in breathing during sleep, known as apnoeas, normally lasting for more than 10 seconds. The main cause of obstruction is the collapse of the walls of the upper airway.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OAS) affects just over 25% of the population and has a negative effect on the quality of life of sufferers. Not only does it disturb their rest during the night, which, in extreme cases, could even lead to death, but also their daily activity, accompanied by drowsiness and chronic fatigue. Even more serious still, Sleep Apnea causes a reduction in oxygen transported by the blood, resulting in arterial hypertension, cardiovascular disease, metabolic and hormonal alterations and an increased risk of accident.