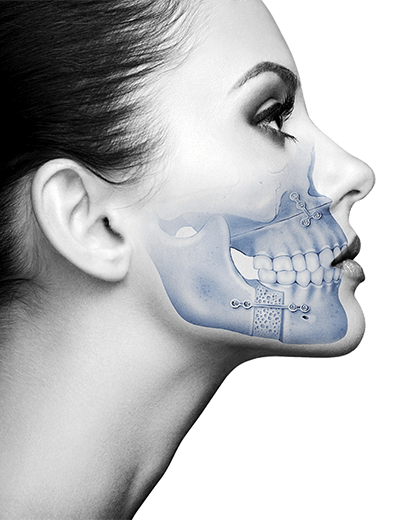
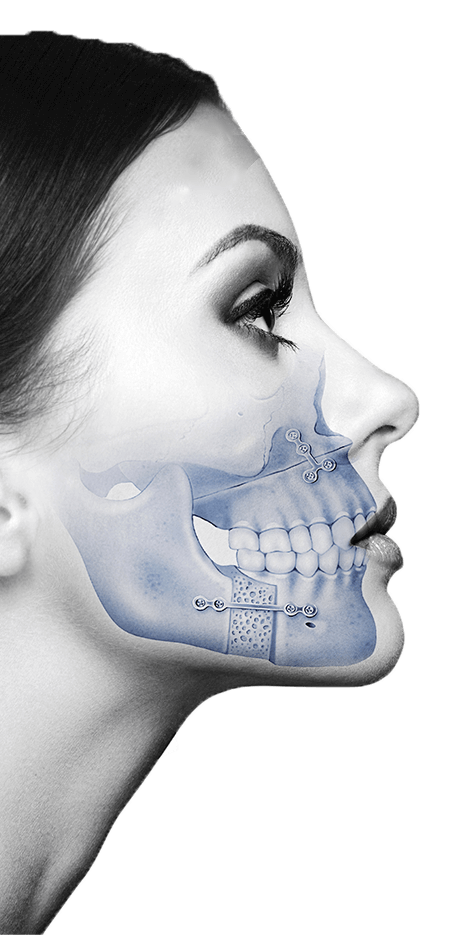
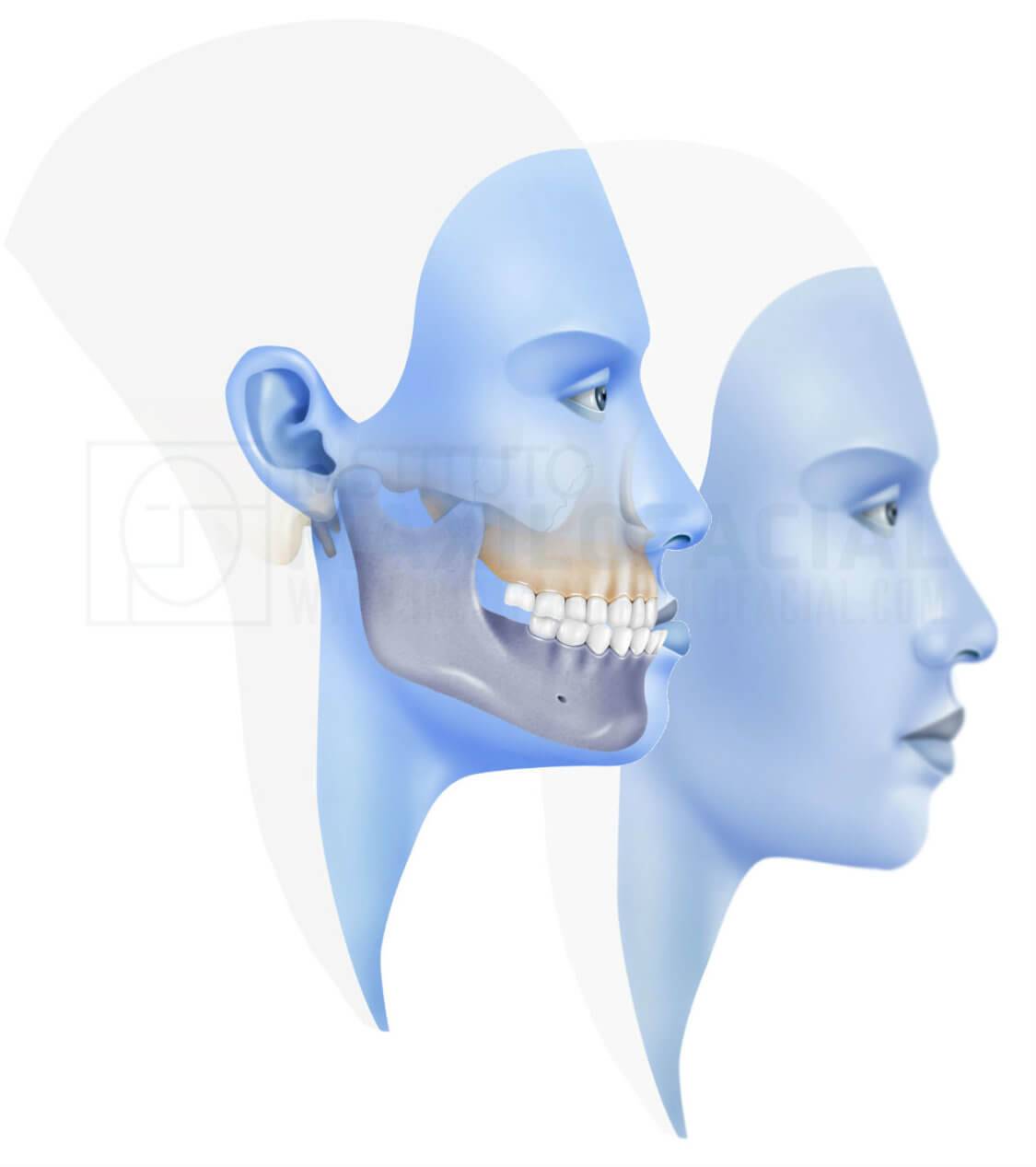
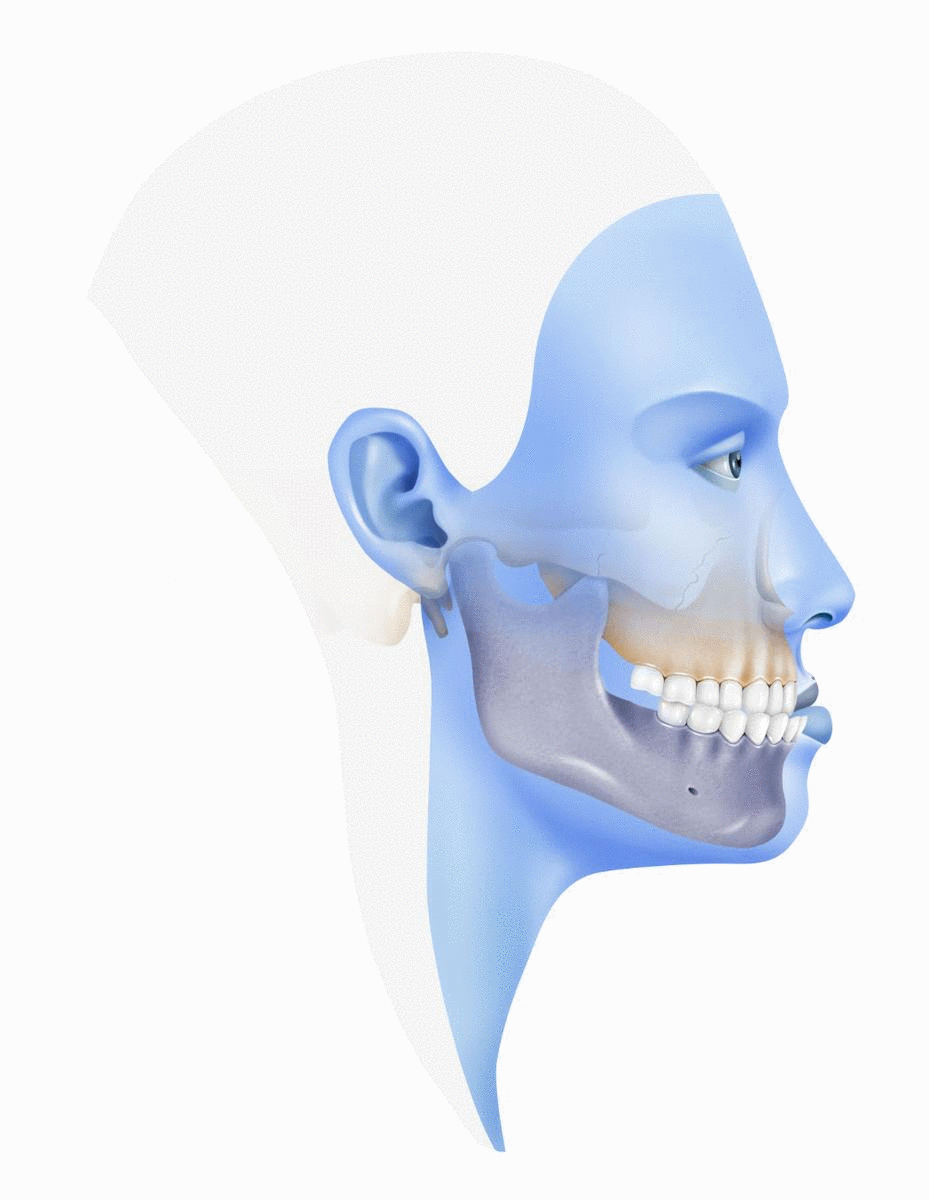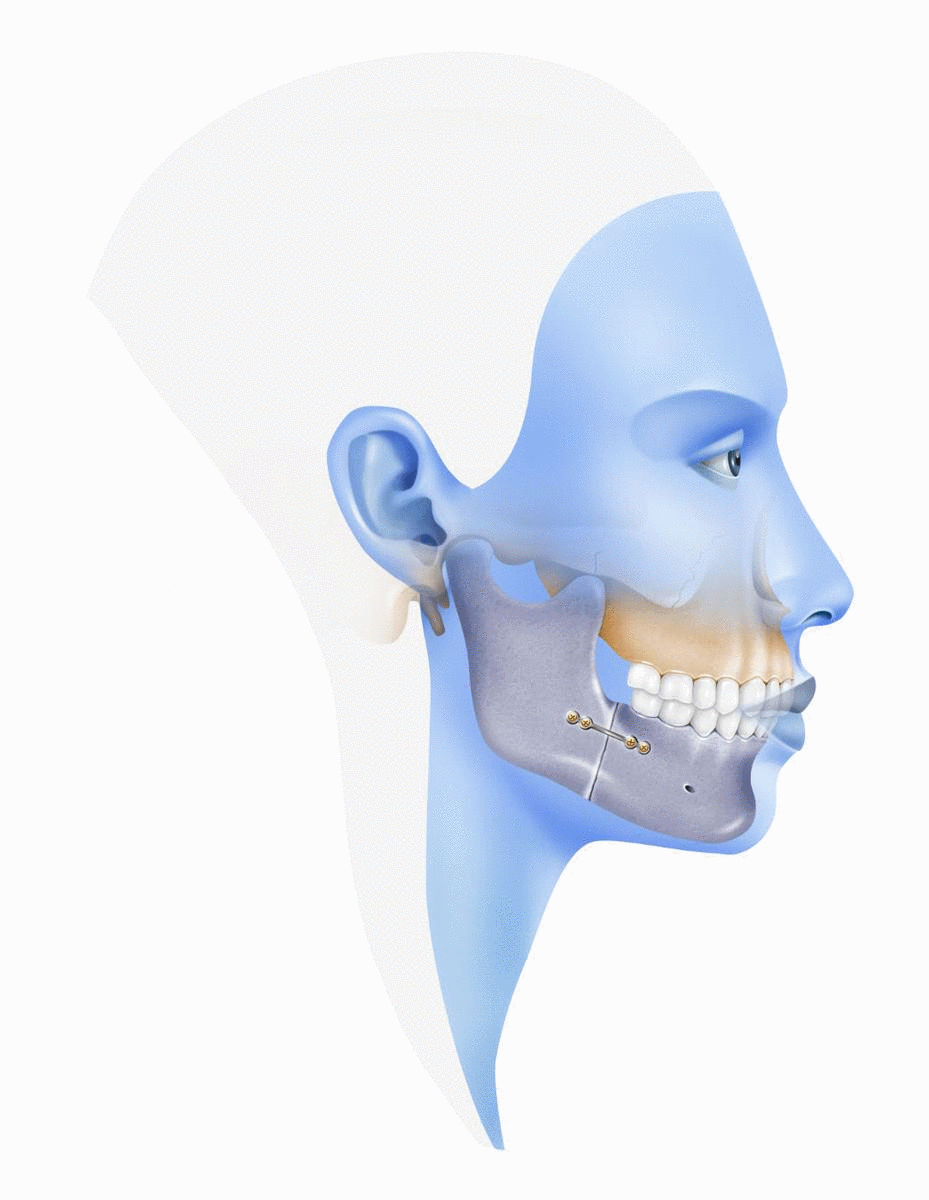
Prognathism, from the Greek pro, "forward" and gnathos, "jaw", is a dentofacial deformity of varied causes, (although with a large genetic component). This malformation is described by the presence of an anteroposterior discrepancy between the jaw and the upper jaw, that is, both bone structures are misaligned with each other.
In cases of mandibular prognathism, the jaw is developed by excess in relation to the maxilla and the inferior dental arch extends forward beyond the superior, causing a Class III malocclusion, also known as underbite.
Class III skeletal malocclusion with a prognatic jaw is one of the most serious maxillofacial deformities, although it is important to underline that this is considered a disorder only if it affects mastication, speech or social function due to a great aesthetic imbalance.