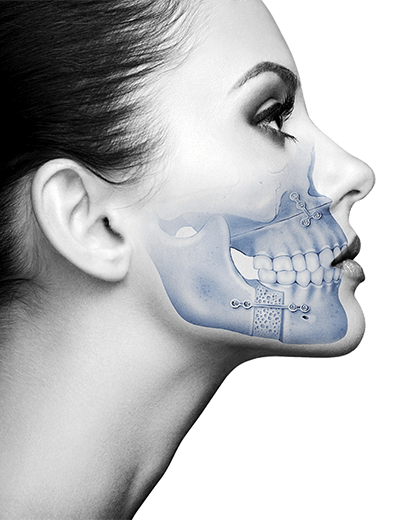
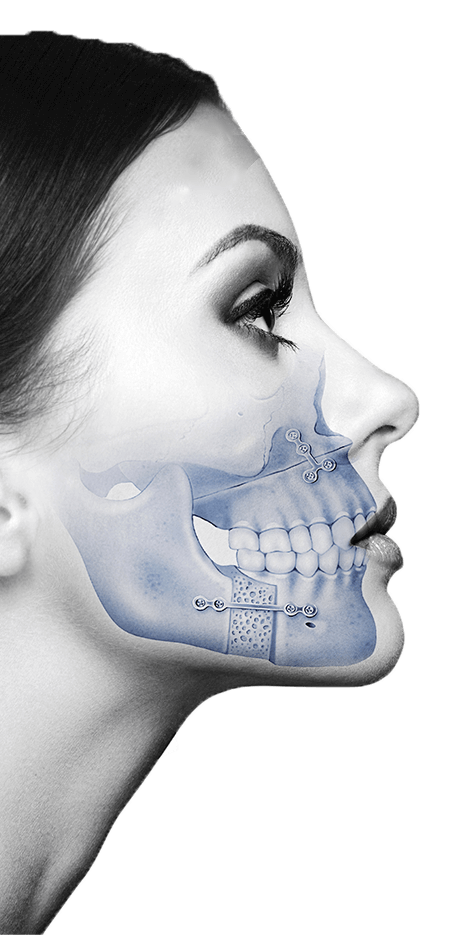
An autogenous transplant of teeth, or autotransplantation, is the transfer of a tooth from its alveolus (cavity that houses a tooth) to a post-extraction alveolus or alveolus prepared surgically in the same person.
Dental autotransplantation can be classified into 3 groups:
- Conventional autotransplantation: surgical movement of a tooth from one site to another in the same patient.
- Intraalveolar autotransplant: surgical movement of a tooth inside its same alveolus, especially useful in important bad positions.
- Intentional reimplantation: used to solve an endodontic problem that can not be solved by conventional methods
The most common situations and with greater probability of success are found when dealing with patients between the ages of 17 and 25 years (since the 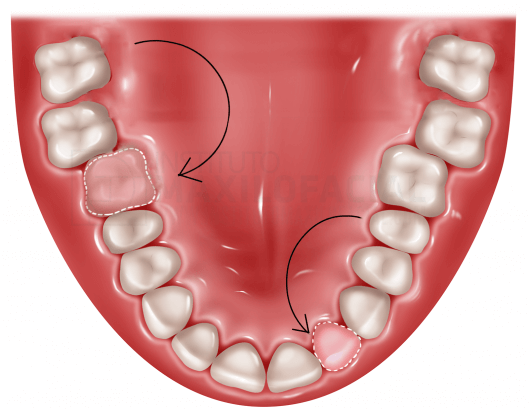 regenerative capacity of the periodontal ligament cells is greater the younger the tooth is, and over the years , this capacity is lost) and with healthy teeth, retained or not, whose roots are not completely formed.
regenerative capacity of the periodontal ligament cells is greater the younger the tooth is, and over the years , this capacity is lost) and with healthy teeth, retained or not, whose roots are not completely formed.
The most used techniques are: the transfer of third molars to the area of the first molars and premolars as substitutes for the incisors.
Complete healing of the periodontal tissue occurs after 8 weeks after the intervention and the success rates of this technique reach up to 90% after 3 to 5 years of follow-up. And this figure is increasing, as the survival of autotransplanted teeth continues to improve thanks to advances in the understanding of bone, periodontal and pulpal healing.
In the Maxillofacial Institute we bet on the autologous technologies whenever possible, since, being based on the patient's own tissues, these treatments eliminate the possibility of rejection and present a healing process much faster than with other treatments.