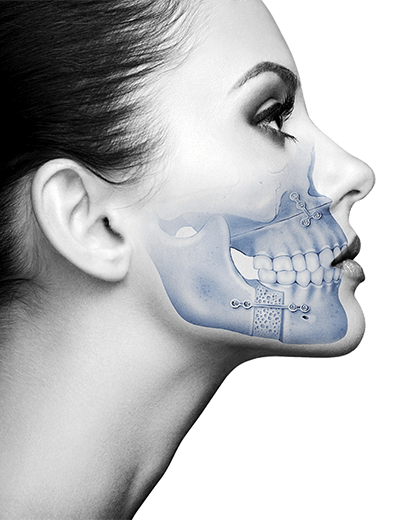
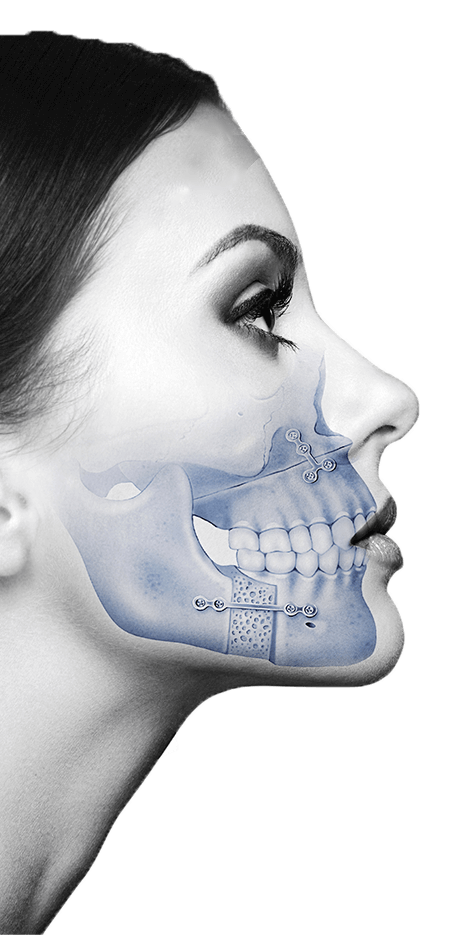
The temporomandibular joint is the only joint we have in the head, and it is located between the jaw and the base of the skull, just in front of the ears. At the junction between these two bones there is a cartilage wafer, called the condyle disc, which smoothens the friction between them and keeps them in place. This condyle disc is encapsulated between ligaments and muscles, and the capsule is filled with synovial fluid (a viscous and transparent fluid found in the joints) and acts as a lubricant.
If for some reason the condyle disc becomes displaced or damaged, it can cause an accumulation of synovial fluid.
The most common reasons for this displacement are strong blows in the area, excessive opening of the mouth or inflammation due to arthritis, although there are other reasons.
The most frequent symptoms of displacement of the condyle disc are:
- difficulty opening and closing your mouth
- chewing pain
- clicks when opening and closing the mouth
- stiffness and pain in the area in front of the ears
- grinding of teeth, especially during sleep
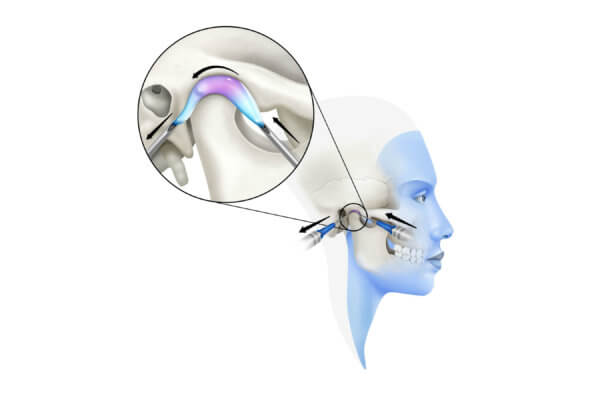
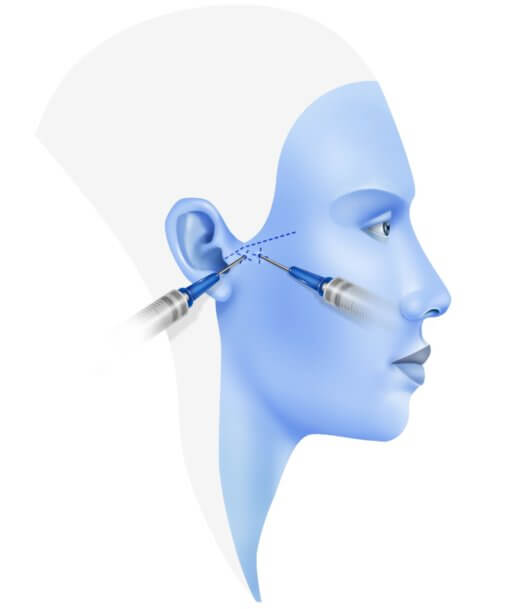 To correct this problem, it is necessary to perform an arthrocentesis of the temporomandibular joint. A TMJ arthrocentesis is a procedure in which the jaw joint is washed with sterile fluid. This procedure involves inserting two small needles into the jaw joint, one of them will allow sterile fluid to be pumped into the joint under pressure, while the other will allow the joint fluid to drain.
To correct this problem, it is necessary to perform an arthrocentesis of the temporomandibular joint. A TMJ arthrocentesis is a procedure in which the jaw joint is washed with sterile fluid. This procedure involves inserting two small needles into the jaw joint, one of them will allow sterile fluid to be pumped into the joint under pressure, while the other will allow the joint fluid to drain. 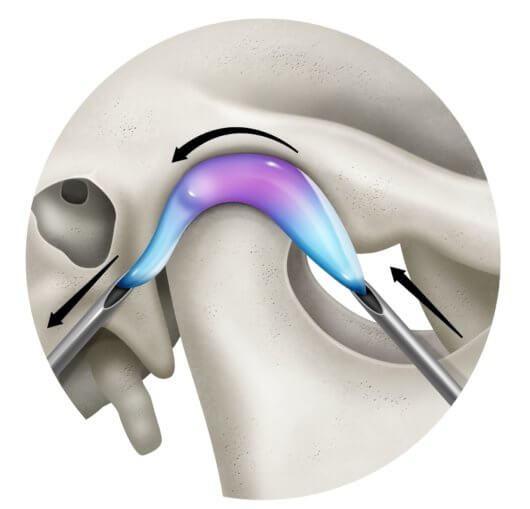 While the jaw is numb, the maxillofacial surgeon will gently manipulate it to try to return the cartilage disc to its normal position within the joint.
While the jaw is numb, the maxillofacial surgeon will gently manipulate it to try to return the cartilage disc to its normal position within the joint.
The goal of ATM arthrocentesis is to put the condyle disc back in place.
TMJ arthrocentesis is generally the first surgical attempt for many patients and is often tested before more drastic options, such as replacement of the jaw joint, a recommended procedure if the patient does not notice improvement with conservative treatments.
If you have discomfort in the area, and need more information on our treatments of the temporomandibular joint, contact our specialists at +34 933933185 or write to international@institutomaxilofacial.com to obtain a diagnosis and a treatment plan.
Related Content:
Why does my jaw make a clicking noise?