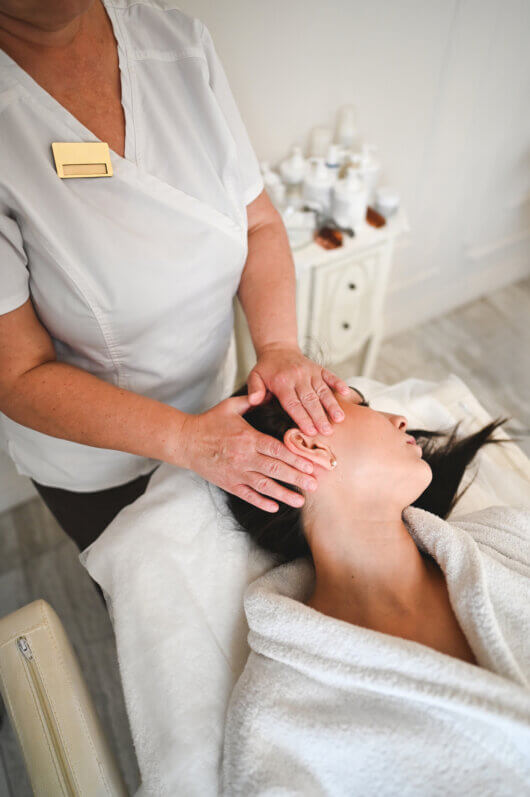
Recovery after maxillofacial surgery, implant treatment, facial trauma, or even a functional problem like bruxism, depends not only on the medical procedure. Maxillofacial physiotherapy is an essential part of the process, as it helps tissues heal better, mobility recover more quickly, and aesthetic and functional results become more stable over time.
At the Maxillofacial Institute, this multidisciplinary approach is integral to our work: surgeons, orthodontists, and specialized physiotherapists work together to offer a faster, more comfortable, and more complete recovery.
What is maxillofacial physiotherapy?
It is a branch of physiotherapy focused on treating disorders related to the face, jaw, neck, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ). It includes manual techniques, therapeutic exercises, and personalized protocols to:
• Restore chewing function and jaw mobility.
• Reduce pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
• Improve muscle symmetry and cervical posture.
• Promote healing and reduce the risk of fibrosis.
The key is that it be performed by professionals with specific training in the maxillofacial area, since working on the facial muscles and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) requires very specific knowledge of biomechanics and anatomy.
In what cases is it especially recommended?
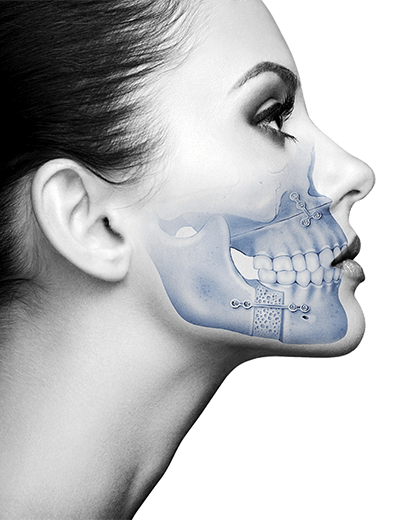
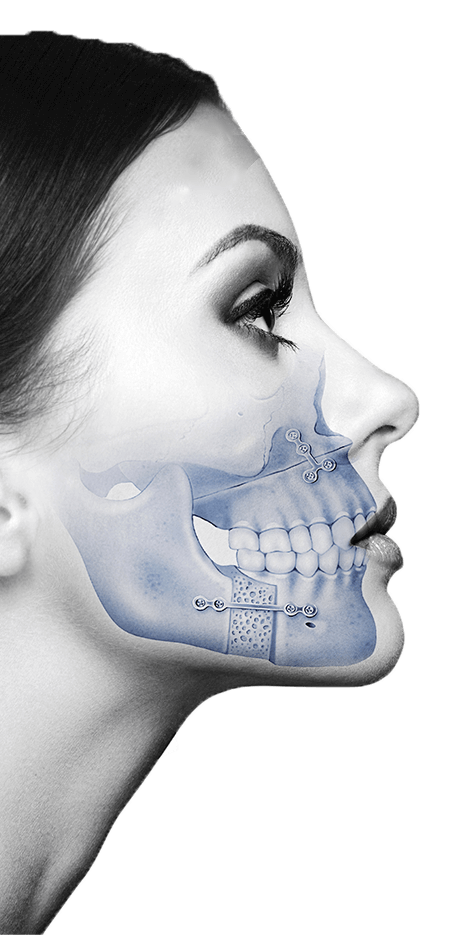
1. Orthognathic Surgery
After mandibular advancement surgery, bimaxillary surgery, or genioplasty, physiotherapy helps to:
• Restore normal mouth opening and prevent functional limitations.
• Reduce inflammation more quickly.
• Retrain the muscles after the structural change.
• Promote adaptation to the new occlusion.
This accelerates the return to normal life and improves sleep quality and respiratory function when the surgery is performed for sleep apnea.
2. Dental Implants and Bone Regeneration
After implant placement, grafting, or sinus lift:
• Reduces discomfort in the masticatory muscles.
• Reduces cervical tension related to bite changes.
• Improves patient adaptation to temporary or permanent prostheses.
It is also useful in patients with severe edentulism who receive zygomatic or pterygoid implants, since the muscles have often spent years compensating for the lack of bone support.
3. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Surgery
In cases of arthroscopy, discectomy, or joint recontouring:
• Physical therapy is key to preventing adhesions and fibrosis.
• The patient is guided toward safe ranges of motion.
• Incorrect muscle patterns that caused the pain are retrained.
4. Bruxism and Myofascial Pain
Here, physical therapy is one of the interventions with the best evidence:
• Reduces masseteric and temporalis muscle contractures.
• Improves jaw mobility.
• Reduces migraines related to jaw tension.
• Addresses postural and breathing habits that influence the condition.
Combined with splints or botulinum toxin, it enhances the results.
5. Facial Trauma
In cases of jaw, orbit, or cheekbone fractures:
• Helps restore facial symmetry.
• Increases flexibility of external and internal scars.
• Restores muscle strength and coordination.
What techniques are used?
Maxillofacial physiotherapy integrates a set of advanced techniques such as:
• Intraoral and extraoral manual therapy
• Guided jaw mobility exercises
• Lymphatic drainage for edema reduction
• Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) mobilization
• Deep myofascial massage
• Neuromuscular re-education exercises
• Cervicocranial postural work
Treatment is always individualized, as each patient presents a different tension pattern.
Benefits for the patient
• Faster and more comfortable recovery
• Less pain and tightness
• Greater mouth opening and jaw mobility
• Improved chewing function
• Reduced inflammation
• More harmonious aesthetic results
• Prevention of long-term complications
In short, physiotherapy allows the patient not only to recover, but to recover fully.
As you can see, maxillofacial physiotherapy is an essential part of the therapeutic process in most maxillofacial treatments. At the Maxillofacial Institute, we have a Maxillofacial Physiotherapy Unit, allowing us to offer an integrated approach that enables patients to achieve a more complete recovery, improved function, and more stable results over time.
Related Content: